Most electric vehicles support fast fasting. A general misconception is that fast charging degrades battery life faster than other mode of charging. Is that true? Is fast charging bad for battery? Let’s find the answer here in this article.
Lithium Ion batteries degrade over time and that’s a general phenomenon. How much battery will degrade, that’s an altogether different discussion as it also depends on how you charge your batteries. If you follow the best practices you can expect up to 5% degradation per year.
Before we learn about whether Is Fast Charging Bad For Battery or not, we need to understand the different ways of battery charging.
How Does Battery Charging Work?
There are two types of charging available for EV batteries. One is AC charging and the other one is DC charging. Please note that the batteries can only take DC power. So when you use an AC charger, the inbuilt converter in the vehicle will convert the AC power to DC power and then charge the battery.
Indian households get AC single-phase power that has 230V and 50Hz frequency. When you use a portable charger ( Even your mobile charger), it converts the AC power to DC power and then charges the battery.
On the flip side, DC charging is fast as it operates on a high voltage range and does not need to convert from AC to DC.
Please note that AC charging communicates with the onboard charger / portable charger but the DC charging communicates directly with the Battery Management System. The BMS can control the voltage and current flowing into the battery to keep these parameters under safe limits.
When you talk about the charging level of EVs, there are three types of charging levels.
- Level -I Charging (AC): Up to 120V
- Level-II Charging (AC): Up To 230V
- Level-III Charging (DC): Above 400V
You can see that the DC charging operates above 400V, so definitely DC charging will be fast. You may wonder that if we do regular DC charging, it may damage EV batteries. Is that the case? Let’s find that out.
Is Fast Charging Bad For Battery?
There is an impact of fast charging on batteries if we consider the degradation. However, the impact is very minimal compared to slow AC charging. This means batteries will degrade both in AC charging and DC charging but the degradation will be a little more in the case of DC charging.
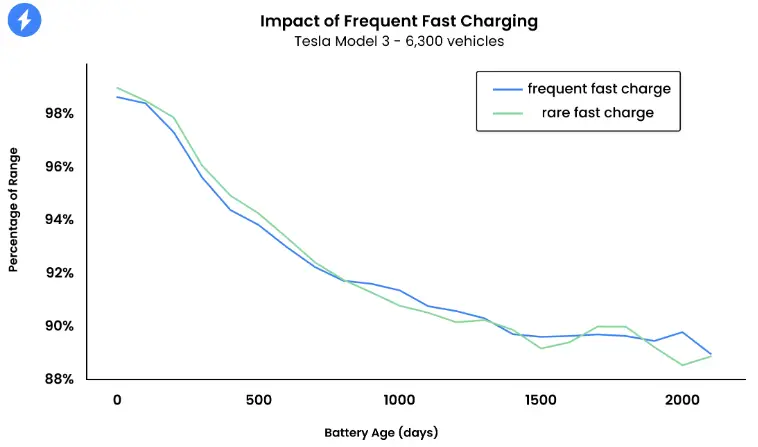
A study by the Idaho National Laboratory on Nissan Leaf cars throughout 50000 miles reveals that level 2 AC charging degrades the battery by 24.5% whereas the cars using the DC charging get battery degradation of 27%. That’s a marginal difference of 2.5% for 50000 miles. Does that make any sense not to use DC charging fearing battery degradation?
Similar studies conducted by Recurrent Motors suggest that there is no noticeable degradation of batteries if we use DC charging regularly. EV batteries are smart enough nowadays to control different parameters that could eventually spoil the battery if those are not operating under safety limits.
One more beauty of DC charging is that it does not generate as much heat as AC charging generates. Generally, we have the misconception that DC charging generates a lot of heat. But that’s not true. It’s AC charging that generates more heat.
Studies reveal that heat is the biggest enemy of batteries and DC charging and the battery management system controls that very well.
So DC charging is not bad, nor does it degrade your battery drastically. 2.5% more degradation than normal AC charging is negligible for a battery that was used for over 50000 miles which is almost one-fourth lifecycle of an electric vehicle.
Conclusion: Is Fast Charging Bad For Battery?
Fast Charging or Direct Current Fast Charging (DCFC) is not bad for batteries. It’s true that if you use DC charging for a prolonged time, your batteries might degrade more but that is very marginal if you compare it with AC charging.
Consider saving 80% of the time charging your battery using a DC charger and sacrificing 2.5-5% more degradation of the battery. It’s a nice tradeoff though. Save 80% time or lose 2.5% more battery capacity.
